Did you know that over 60% of occupations could see at least 30% of tasks automated with current automation technologies? It’s not the future—it’s now. From self-checkout machines at the grocery store to robots assembling cars, automation technology is reshaping the world around us in ways you might not even realize. This article lifts the curtain on where these systems already exist, how they work, and what that means for our daily lives.
Unlocking the New Era: Automation Technology Facts That Will Surprise You
The world is already teeming with automation technology, quietly powering everything from the factories that build our clothes to the predictive tools on our smartphones. Automation technologies are transforming the very core of how businesses run, products are made, and information is processed. Some of these breakthroughs might even be at work in your own home or workplace right now. In fact, the global market for automation technology is booming, with experts predicting nearly $300 billion in industry spending by 2026. Robots, machine learning, and intelligent control systems are replacing repetitive, dangerous, or highly precise tasks, freeing up people for higher-value work.
You might be surprised to find out that automation extends well beyond industrial robots: it touches business process automation, quality control in manufacturing, healthcare diagnostics, and even your favorite streaming service recommending the next show to watch. As automated systems continue to spread, understanding their underlying principles—and their broad-reaching impact on various industries—has never been more essential. Step into this new era as we break down the astonishing facts, essential types, and real-life examples of automation taking shape all around us.
Did you know that over 60% of occupations could see at least 30% of tasks automated with current automation technologies?
What You’ll Learn About Automation Technology
- The fundamentals and evolution of automation technology
- Key types of automation technologies and where they are used
- Real-world examples of automation technology in action
- How automation is shaping industries and society
- The differences between automation technology, artificial intelligence, and machine learning
What Is Automation Technology?

Defining Automation Technology and Its Scope
Automation technology refers to the use of systems, machines, and software that accomplish tasks or operate processes with minimal human intervention. This encompasses everything from production machines in factories, to intelligent algorithms managing online banking transfers. At its core, automation is the application of technology to perform repetitive, hazardous, or complex tasks that were once handled by people. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, automation technologies are becoming more adaptive and capable of handling a wider range of scenarios.
The scope of automation technology is vast, covering tangible hardware like industrial robots and sensors, as well as software-driven solutions such as robotic process automation and business process automation. These technologies aim to streamline workflows, improve accuracy, reduce costs, and increase productivity and efficiency. From automated quality control checks in manufacturing, to chatbots providing customer service online, the reach of automation is growing daily. This broad definition underlines its impact across various industries, each reaping unique benefits tailored to its needs.
How Automation Technologies Drive Today’s World
Today, automation technologies are everywhere—quietly boosting efficiency in ways we don’t always notice. Take supply chain management, for example. Automated systems can track and manage inventory in real time, reduce human error, and speed up delivery times. In customer service, technologies like chatbots and AI-driven assistants handle queries faster than ever before, improving response time and consistency. In everyday life, home automation lets you control lighting, temperature, and security with the tap of a screen or voice command.
The rapid integration of automation technology is driving down labor costs while raising the bar for quality and innovation. Businesses use feedback control and predictive maintenance to minimize downtime and pre-empt machine failure. Even creative industries now use automation for tasks such as image enhancement, video editing, and algorithmic music composition. Ultimately, automation empowers organizations and individuals alike to focus on creativity, strategy, and customer engagement, rather than rote manual processes.
A Brief History: From the Industrial Revolution to Modern Automation Technologies
The Leap from Mechanical to Digital: The Fourth Industrial Revolution
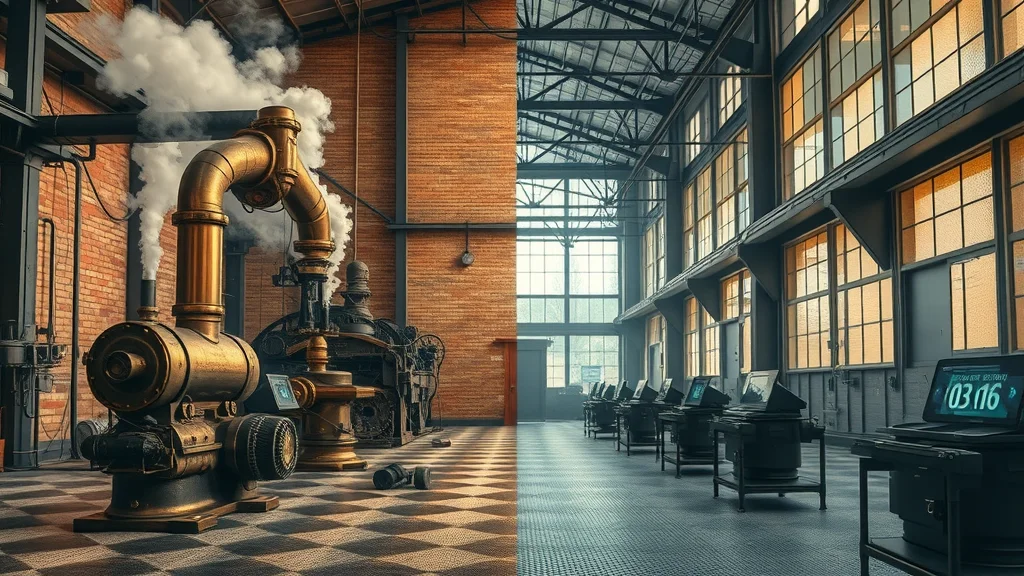

To understand modern automation technology, it helps to look backward. The Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries introduced the first wave of automation, with steam engines and mechanical looms drastically increasing production. As electricity and simple control systems emerged, factories became more efficient and less reliant on manual labor. The arrival of computers in the 20th century triggered a dramatic shift: machines could now be programmed to operate with greater speed and precision.
We are now in the era known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0. This stage is driven by the convergence of digital, physical, and biological systems. Here, automation technologies harness the power of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced robotics. These digital tools enable automated systems to self-optimize, communicate, and adapt, transforming how manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and even customer service operate at the most fundamental level.
Milestones: How Automation Technology Evolved
Some key milestones have supercharged the speed and scale of automation. The invention of the numerical control (NC) machine tool in the 1950s allowed manufacturing processes to be automated with unmatched precision. By the 1980s, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and computer-integrated manufacturing set the stage for today’s flexible automation systems. The rise of industrial robots further increased the reach and flexibility of automated manufacturing processes.
More recently, software-based robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analytics have expanded the reach of automation to office tasks, financial markets, and beyond. These advancements reduce manual intervention, streamline tasks that require minimal human decision-making, and set new standards for speed and accuracy. Each innovation along this timeline has pushed automation technology into new sectors, transforming daily business operations and raising expectations for efficiency and quality control.
Types of Automation Technology: Pathways to Progress
The Four Main Types of Automation Technology
Understanding the major types of automation technology is crucial for recognizing how and where these systems are applied. The four main categories—fixed automation, programmable automation, flexible automation, and integrated automation—define how tasks are handled in various industries and set the stage for widespread adoption. Fixed automation is typically found in high-volume environments where the production process never changes, like bottling plants. Programmable automation uses computer instructions to allow changes in production, suitable for batch processing.
Flexible automation takes adaptation a step further, letting systems switch tasks rapidly without halting operations—think of modern car manufacturing lines swapping models within minutes. Integrated automation combines all processes, data, and controls into a seamless whole, often monitored through digital dashboards and managed by AI-driven analytics. Choosing the right form of automation is all about balancing productivity, efficiency, cost, and adaptability for a specific process or business goal.
| Type | Features | Best Use Example | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Automation | Specialized equipment, high initial cost, high production volume | Bottling plant, car assembly line for a single model | Low |
| Programmable Automation | Programmable sequence, batch production, moderate cost | Batch production of machine tools or custom parts | Medium |
| Flexible Automation | Quick changeover, smaller batches, computer-controlled | Automotive lines switching models, electronics | High |
| Integrated Automation | Unified digital control, real-time feedback, AI integration | Smart factories, complex logistics | Very High |
Process Automation vs. Robotic Process Automation
While process automation and robotic process automation (RPA) might sound similar, there are key differences. Process automation typically refers to automating physical, industrial, or technical tasks—like a control system running conveyor belts in a manufacturing process. It relies on hardware, sensors, and automated systems to manage repetitive workflows efficiently and safely, minimizing human intervention.
Robotic process automation (RPA), by contrast, is a software solution focused on digital business tasks: data entry, invoice processing, or scheduling. RPA doesn’t use physical robots; instead, it simulates human actions within software, significantly reducing errors and increasing productivity and efficiency. Together, both forms revolutionize their specific domains—a manufacturing plant might use both industrial robots and RPA to streamline production and office functions alike.
Core Components: How Does Automation Technology Work?
Key Hardware in Automation Technology (Sensors, Actuators, Robots)

Behind the scenes of every automated system are essential hardware components. Sensors detect physical properties such as temperature, light, movement, or pressure, feeding real-time information into the control system. Actuators then convert electrical signals into mechanical movement—like opening a valve or moving a robotic arm. Together, they form the backbone of any functional automation setup, ensuring accuracy and quick response time.
Modern industrial robots combine these elements, offering remarkable flexibility and range. For example, a machine tool equipped with sensors and responsive actuators can adapt instantly to changing product specs or halt automatically if something seems off. In many settings, these hardware pieces are networked with the internet of things (IoT), so data can flow seamlessly between systems for maximum increase productivity and safety. Every touchpoint, from the sensor tip to the robot endpoint, is engineered for reliability and speed, making automation the powerhouse of modern industry.
Software Revolution: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Automation
Though hardware powers the movement, it’s the rapid advance of software—especially in machine learning and artificial intelligence—that’s putting next-level automation within reach. Machine learning algorithms help systems learn from data and adjust their behavior without step-by-step reprogramming, making real-time feedback control possible in highly dynamic environments. In manufacturing, for example, AI-driven analytics can predict equipment failure before it happens (predictive maintenance), saving time and costs.
Artificial intelligence is woven into everything from voice-activated assistants to complex logistics platforms. AI can make sense of massive datasets, optimize business processes, and uncover trends that would take humans far longer to spot. When paired with hardware, AI turns a standard production machine into a smart, self-monitoring automated system—capable of optimizing itself on the fly. The blend of AI and machine learning with automation offers nearly limitless possibilities for various industries, reshaping not only how work is done, but also what’s possible.
Spotlight on Industrial Automation: Game Changer for Manufacturing
Industrial Automation and Quality Control
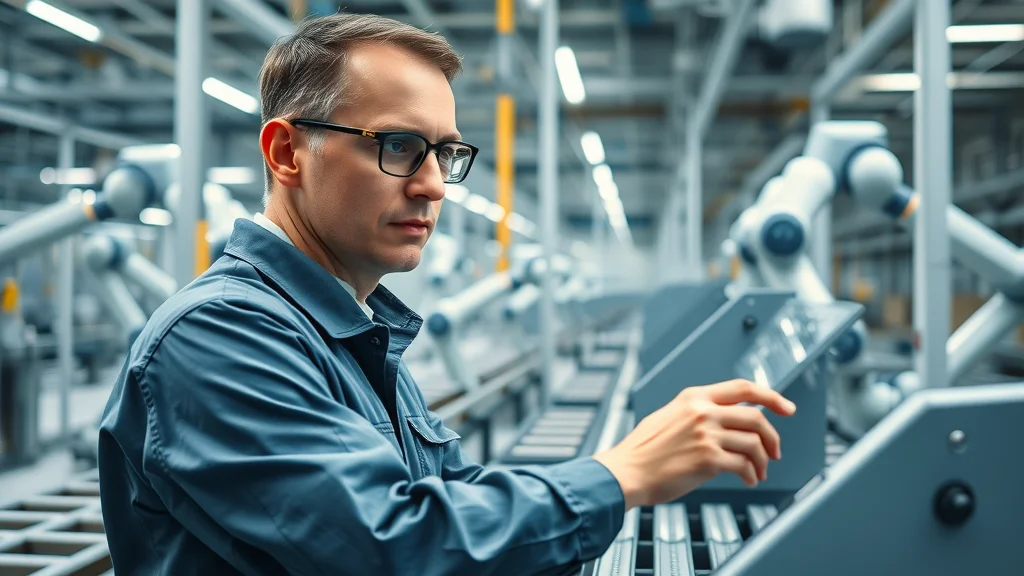

Industrial automation has fundamentally changed the landscape of manufacturing. Smart control systems monitor production machines for consistency, speed, and precision—often delivering error rates far lower than what’s possible with human labor alone. Quality control, in particular, has become more rigorous thanks to industrial robots equipped with vision systems that inspect every product for defects in real time.
Automated quality control systems use high-speed cameras, lasers, and AI-based algorithms to spot issues and make adjustments in milliseconds, ensuring every item meets strict standards. This leads to fewer recalls, less waste, and higher consumer trust. And, as the technology evolves, manufacturers are able to gather more data to drive process improvements and further boost productivity and efficiency. These innovations have made industrial automation indispensable for global supply chains striving for excellence and consistency.
Case Studies: Advanced Automation Technologies in Modern Plants
Across different sectors, automation solutions show dramatic results. In automotive manufacturing, assembly lines feature hundreds of industrial robots seamlessly building, welding, and painting vehicles at speeds and levels of accuracy humans can’t match. Electronics plants rely on flexible automation to rapidly switch between products as market demand shifts, cutting turnaround time and ensuring quality.
In food processing, automated quality control ensures even packaging and eliminates contaminants, meeting regulatory requirements without the need for constant human monitoring. Pharmaceutical manufacturing uses process automation and AI to manage precise formulations and real-time compliance documentation, reducing delays and errors that could risk public health. These case studies prove that integrating automation technology not only increases output but also innovates the way industries think about safety, quality, and adaptability.
"Industrial automation technology has cut defect rates by over 50% and improved quality control outcomes globally."
Business Process Automation: Efficiency Beyond Factories
From Office Tasks to Customer Service – Automation Technology at Work

It’s not just manufacturing that’s been changed by automation—offices are experiencing their own quiet revolution. Business process automation (BPA) uses specialized software to handle routine workflows: processing invoices, scheduling appointments, onboarding new employees, and much more. Tools like RPA bots can interact with multiple applications as if they were human users—copying, pasting, filing, and even making calculations in the background while your team focuses on value-added projects.
Customer service automation, powered by AI chatbots and virtual agents, responds to queries at any hour of the day, reducing wait times and ensuring consistent answers. This tech can escalate more complex issues to live agents, providing a seamless experience. Thanks to automation technology, business processes are faster, more accurate, and less costly, fueling a new era of productivity and efficiency whether you’re in HR, finance, IT, or customer support.
Machine Learning and AI: Transforming Business Process Automation
Layering in machine learning supercharges business process automation. Smart algorithms can flag fraudulent transactions in real time, analyze massive volumes of unstructured text (like emails or feedback forms), and even provide real-time decision support to salespeople or financial analysts. AI tools can automate the review of contracts and legal documents, saving weeks of manual work.
Advanced automation technologies now deliver predictive insights—such as which leads are likeliest to convert or when an employee might need extra training. As a result, companies become more competitive while employees engage in higher-level, creative problem-solving instead of repetitive grunt work. This transformation represents one of the most exciting frontiers in automation, with AI-driven process automation promising revolutionary gains across every aspect of modern office life.
Where Else Is Automation Technology Already Present? Real-World Examples
- Healthcare: Robotic surgeries, smart diagnostics, and automated drug dispensing improve patient safety and speed up recovery times.
- Retail: Automated checkouts, AI-powered recommendations, and supply chain robots streamline the entire shopping journey from warehouse to store.
- Logistics: Warehouse robots, automated packing, and delivery drones enable real-time order fulfillment and rapid delivery, often without human hands involved.
- Finance: Automated trading algorithms, fraud detection systems, and digital loan approvals cut paperwork and increase reliability in banking and investing.

Future Trends: Where Is Automation Technology Heading Next?
Emerging Automation Technologies and Research
The future of automation technology is brimming with possibilities. The next wave includes collaborative robots (“cobots”) that work safely alongside humans, adaptive AI that learns from fewer examples, and edge-computing systems that operate closer to the source of data for near-instant response time. Scientists and engineers are also working on self-healing networks, fully autonomous vehicles, and integrated automation that links every step of production—from raw material sourcing to delivery—in real time.
Research projects worldwide are exploring how automation can be used for environmental monitoring, disaster response, and even creative arts. Rapid advances in machine learning mean that tasks long considered the sole domain of humans—like diagnosing rare diseases or composing music—are now within reach for smart automated systems. As investment in research and development grows, these new tools will transform businesses’ ability to respond to market shifts, consumer needs, and societal challenges with agility and insight.
Potential Societal Impacts: Jobs, Skills, and the Human Factor

While the rise of automation technologies brings tremendous benefits, it also raises questions about the future of work. Some jobs will evolve or even disappear, but others—especially those involving creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving—will become more important. The most successful workers will be those who adapt their skills, focusing on collaboration with automated systems rather than competition. Lifelong learning, digital literacy, and critical thinking are becoming essential in this new environment.
On the broader scale, automation has the power to improve workplace safety by eliminating dangerous tasks, enhance accessibility for people with disabilities, and drive economic growth through increase productivity. However, it’s crucial for businesses and societies to balance the relentless march of technology with thoughtful policies, training, and ethical considerations. Ensuring that automation amplifies human capability, rather than replacing it entirely, is key to building a smarter, fairer, and more innovative future.
"Automation technology isn’t about replacing people – it’s about amplifying human potential."
People Also Ask About Automation Technology
What is the automation technology?
Automation technology refers to systems, machines, and software that operate tasks or processes with minimal or no human intervention, leveraging tools like robotics, sensors, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
What are the 4 types of automation?
The four key types include fixed automation, programmable automation, flexible automation, and integrated automation – each suited to different production or business needs.
What is automation and examples?
Automation is the use of technology to perform tasks traditionally done by humans. For example: robotic arms in car manufacturing, chatbots in customer service, and machine learning algorithms in financial trading.
Is automation a form of AI?
Some automation involves artificial intelligence, especially in advanced adaptive systems, but not all automation is AI—it can also include basic rule-based machines.
Expert Insights: Key Quotes on Automation Technology
"Automation technologies represent both an opportunity and a responsibility. Their potential is only matched by our need to guide their implementation wisely." – Industry Expert
Key Takeaways: What You Need to Know About Automation Technology
- Automation technology is already transforming a wide range of industries.
- There are multiple types of automation technologies, each with distinct uses.
- Success with automation depends on smart integration with people and processes.
- Automation and AI are linked but not identical; each has unique capabilities and limitations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Automation Technology
-
How can businesses get started with automation technology?
Begin by identifying repetitive or time-consuming tasks. Research suitable automation tools or consult industry experts to implement the best-fit solution for your workflow. -
What skills will be most in demand as automation technologies expand?
Skills in digital literacy, programming, data analysis, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence will be highly valued as technology continues to evolve. -
Are there risks to be aware of when implementing automation technology?
Yes, including data security, system errors, workforce disruption, and the need for ongoing training. Careful planning and ethical guidelines help address these risks. -
What are the ethical considerations of widespread automation?
Fairness, transparency, and accountability are critical—businesses must ensure automation enhances, not diminishes, human dignity and opportunity.
Share Your Thoughts on the Future of Automation Technology
We'd love to hear what you think about this! Please add your comments below...
In summary: Automation technology is transforming businesses and daily life. Embracing smart integration and continual learning is key to thriving in our automated future.
To deepen your understanding of automation technology, consider exploring the following authoritative resources:
- “Automation | Technology, Types, Rise, History, & Examples”
This comprehensive article from Britannica delves into the fundamentals of automation, its historical development, and its impact on various industries. (britannica.com)
- “What Is Automation?”
IBM provides an insightful overview of automation, discussing its applications across different sectors and the benefits it offers to businesses. (ibm.com)
These resources offer valuable insights into the evolution and current state of automation technology, enhancing your grasp of its significance in today’s world.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 










Write A Comment